
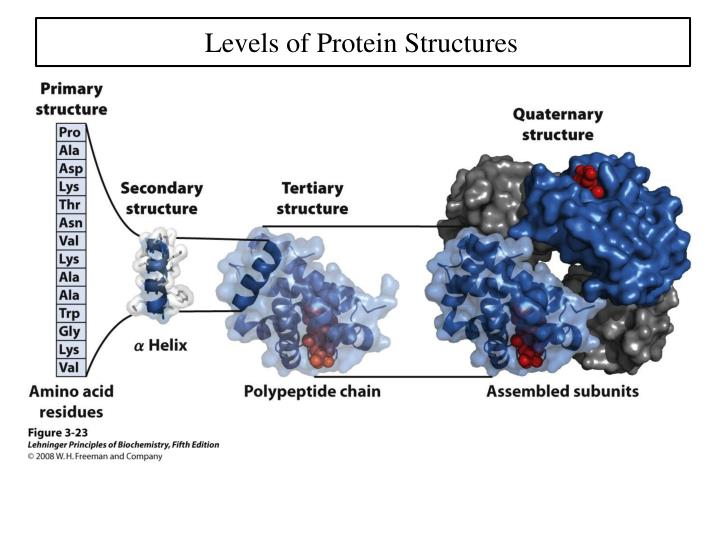
In sickle cell anemia, the hemoglobin β chain has a single amino acid substitution, causing a change in protein structure and function.
A change in the nucleotide sequence of the gene’s coding region may lead to adding a different amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain, causing a change in protein structure and function. The gene encoding the protein ultimately determines the unique sequence for every protein. It is also noted which one can create a disulfide bond. The table includes the full name and abbreviations of each amino acid as well as their charge (positive, negative, or neutral). Amino Acid Characteristics Amino AcidĪ list of the 20 amino acids common in all living things. Note that these bonds are not as strong as what is created between amino acids when an amino acid chain is created, but these bonds are strong enough to hold the shape of the protein. There are other properties that also influence a protein’s shape, such as the amino acid’s polarity. See the table below for a list of all 20 amino acids and their charges. Also, the amino acid called cysteine contains sulfur and sulfurs easily bind with each other, creating a “disulfide bond.” Because of this, cysteines bind with other cysteines. Negatively charged amino acids bind with positively charged amino acids (neutrally charged amino acids are not affected). For instance, each amino acid is negatively (-), positively (+), or neutrally (N) charged. The chemical properties of the amino acids determine how this shape occurs. This is caused by the chemical properties of the amino acids. Protein StructureĪs seen in the image above, a strand of amino acids folds on itself, creating a unique shape in the tertiary structure of the protein. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in organisms. A polypeptide chain is composed of amino acids.
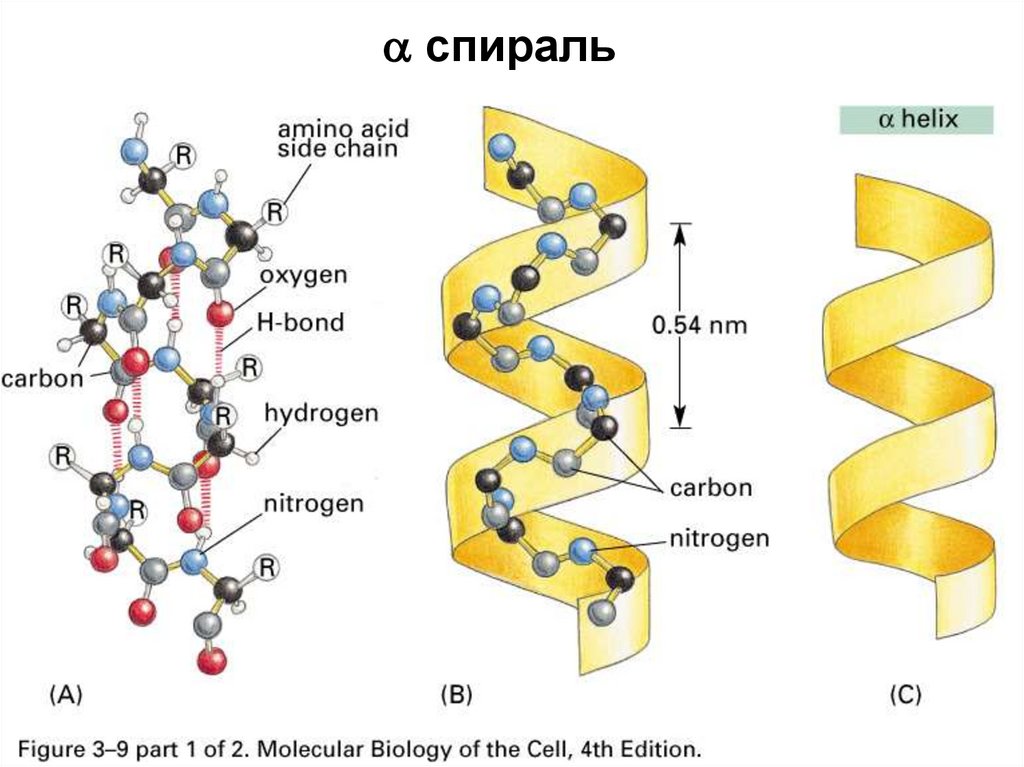
A protein is a folded polymer structure, which contains a polypeptide chain (polymer), which contains amino acids (monomers). Below are two illustrations depicting the relationship between amino acids and polypeptides. Nine of these are essential amino acids in humans because the human body cannot produce them and we obtain them from our diet. As we mentioned, there are 20 common amino acids present in proteins. Scientists use the name “amino acid” because these acids contain both an amino group and a carboxyl-acid group in their basic structure. A polypeptide folds into a 3D structure called a protein. Monomers are molecules that can bind into long chains-these long chains are called “polymers.” In other words, a polymer (“poly” = many) is made of monomers (“mono” meaning “one”).Īmino acids are the monomers that comprise polypeptides (polypeptides being the polymers).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
